Beggars in Uttarakhand
Beggars in Uttarakhand are often seen in urban areas, pilgrimage sites, and tourist destinations like Haridwar, Rishikesh, and Dehradun.
Beggars in Uttarakhand are often seen in urban areas, pilgrimage sites, and tourist destinations like Haridwar, Rishikesh, and Dehradun. Many beggars, including migrants from neighboring states, struggle with poverty, lack of employment, and limited access to education and healthcare. In spiritual centers, begging is sometimes linked to religious practices, with people seeking alms for blessings. Despite government and NGO initiatives for rehabilitation, the problem persists due to socio-economic challenges, making it a complex issue requiring long-term solutions such as job creation, education, and awareness.
Uttarakhand, known for its majestic mountains, tranquil landscapes, and revered pilgrimage destinations, draws millions of tourists and devotees every year. However, amidst its natural beauty and spiritual aura, the state faces an ongoing issue: begging. While begging is not unique to Uttarakhand, its prevalence in popular religious and tourist hubs highlights deeper socio-economic concerns that need urgent attention.
The Roots of Begging in Uttarakhand
Begging in Uttarakhand is a multifaceted issue that arises from a combination of economic hardship, migration, and cultural factors. Despite the state’s growing tourism industry and its role as a religious hub, many residents face poverty and unemployment, leading some to resort to begging as a survival strategy. Additionally, Uttarakhand’s economic disparity, especially in rural areas, exacerbates the situation, as people from disadvantaged backgrounds migrate to urban areas in search of opportunities, often without success.
Tourism and Pilgrimage Impact
Uttarakhand’s religious significance plays a pivotal role in the prevalence of begging. Pilgrimage sites like Haridwar, Rishikesh, Kedarnath, and Badrinath attract millions of devotees each year, many of whom offer alms in the belief that giving to the poor in holy places brings spiritual merit. Beggars often target these sacred locations, relying on the generosity of pilgrims. This cultural practice of giving alms, while rooted in faith, perpetuates begging in these areas. As tourists and pilgrims throng these cities and towns, beggars are seen in greater numbers, especially in temple precincts and surrounding areas.
The high influx of tourists in places like Dehradun, Mussoorie, and Nainital has further fueled the practice of begging. These tourist hubs see a rise in beggars who appeal to the compassion of visitors, often with emotional or religious pleas. Unfortunately, this creates a vicious cycle, as the ease of obtaining alms encourages more people to resort to begging in popular areas.
Migration and Economic Hardship
In addition to the religious and tourist influences, economic factors contribute significantly to begging in Uttarakhand. The state experiences a large influx of migrants, particularly from neighboring states such as Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Nepal. While many migrants come in search of better livelihood options, they often find themselves without stable jobs or affordable housing. With limited access to education, healthcare, and basic services, they are left vulnerable, with begging becoming a means of survival.
For many people in rural parts of Uttarakhand, poverty remains an ongoing issue. The lack of agricultural sustainability, underdeveloped infrastructure, and limited industrial growth leave people with few opportunities to earn a living. As a result, begging becomes a default option for those unable to find stable work in urban centers.
Cultural and Religious Dimensions of Begging
In Uttarakhand, begging is not always viewed negatively. In some cases, it is seen as part of the religious or cultural fabric of the region. Many beggars in pilgrimage areas, such as Haridwar and Rishikesh, are elderly individuals or religious mendicants who have adopted begging as part of their spiritual journey. These individuals may view begging as a way to surrender to God, with their faith guiding their actions.
Additionally, religious beliefs play a role in the perpetuation of begging in Uttarakhand. Devotees who visit sacred sites often give alms as a way to earn blessings or merit in the eyes of the divine. This act of charity becomes deeply ingrained in the local culture, making it difficult to challenge the practice of begging, as it is viewed by many as a virtuous act rather than a social problem.
Government and NGO Initiatives
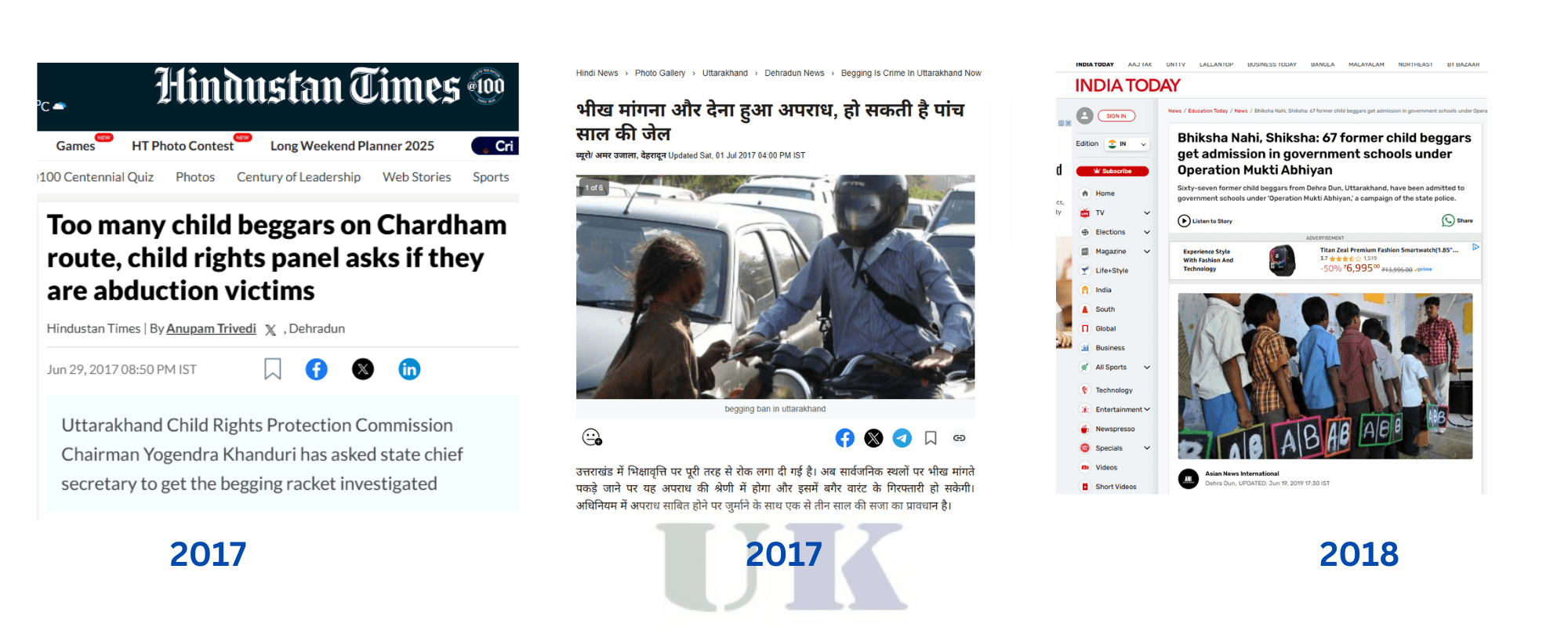
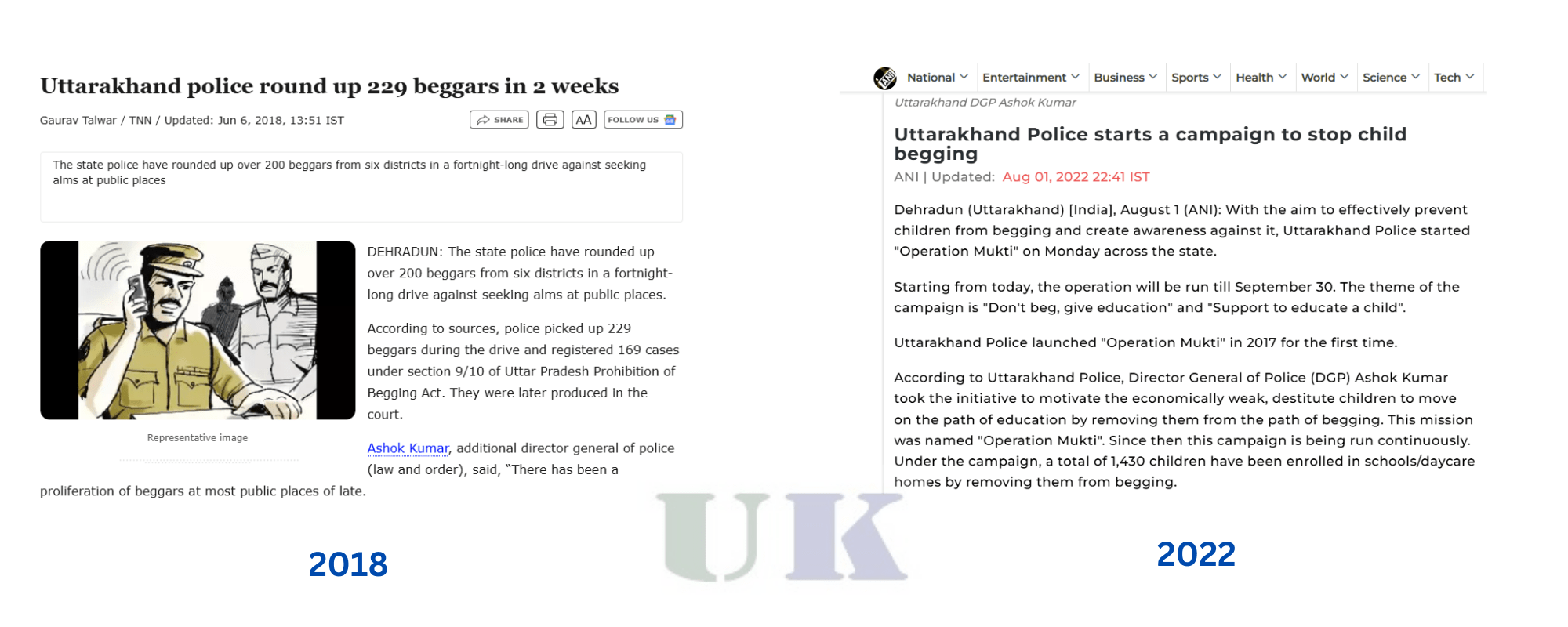
The government of Uttarakhand and various non-governmental organizations (NGOs) have taken steps to address the issue of begging, but challenges remain. Over the years, the government has implemented programs aimed at reducing begging through rehabilitation, education, and social welfare schemes. One of the major initiatives has been the establishment of shelter homes and rehabilitation centers for beggars, offering them the opportunity to rebuild their lives with vocational training and support services.
However, the implementation of such programs faces significant hurdles. Many beggars, especially those involved in religious begging, resist leaving the streets and accepting help. The state also faces difficulties in providing adequate resources and support for such programs, with funding often being insufficient.
NGOs working in Uttarakhand have focused on providing immediate relief to beggars, including shelter, food, and healthcare. Some organizations have also offered rehabilitation programs, teaching beggars vocational skills and helping them reintegrate into society. These efforts, however, have limited reach and impact, particularly in remote areas and regions with high levels of poverty.
Challenges in Addressing Begging
Addressing begging in Uttarakhand requires a comprehensive approach that acknowledges the economic, cultural, and religious factors involved. Simply attempting to eradicate begging without addressing the root causes, such as poverty, migration, and unemployment, is unlikely to produce sustainable results.
One of the main challenges is the lack of detailed data on the extent of begging in the state. There is no clear understanding of how many people are involved in begging or the reasons behind their actions, making it difficult to develop effective policies. Moreover, many beggars view their situation as temporary or voluntary, making it hard to persuade them to seek help.
A Path Forward
To effectively tackle begging in Uttarakhand, it is essential to focus on long-term solutions that address the underlying socio-economic conditions. Initiatives should aim to provide better employment opportunities, particularly in rural and economically disadvantaged areas. Additionally, education and healthcare must be made more accessible to marginalized communities to break the cycle of poverty.
Public awareness campaigns can also play a crucial role in changing attitudes toward begging. Encouraging responsible charity, such as donations to trusted NGOs or social welfare programs, can reduce the dependence on begging for survival. Further, the state can invest in improving infrastructure, creating jobs, and promoting self-reliance through vocational training and skill development programs.
FAQs on Beggars in Uttarakhand
Why is begging common in Uttarakhand?
Begging in Uttarakhand is primarily driven by poverty, migration, and the tourism industry. Popular pilgrimage sites and tourist destinations attract beggars, with many individuals seeking alms from pilgrims and tourists. Economic hardships and a lack of employment opportunities also contribute to the prevalence of begging.
How does tourism impact begging in Uttarakhand?
Tourism, especially around sacred pilgrimage sites like Haridwar and Rishikesh, fuels begging. Many beggars target tourists and pilgrims, as giving alms is often seen as a spiritual merit. The influx of visitors increases the visibility of beggars in these areas, sustaining the practice.
Are beggars in Uttarakhand always in need?
While many beggars are genuinely in need due to poverty, some are religious mendicants or individuals who have chosen begging as a lifestyle tied to spiritual beliefs. In pilgrimage areas, begging can be part of the religious tradition where beggars are seen as seeking blessings.
What is the government doing to address begging in Uttarakhand?
The Uttarakhand government has implemented several initiatives to address begging, including rehabilitation programs, shelter homes, and vocational training. The government works with NGOs to provide support, education, and healthcare services to help beggars reintegrate into society.
Are there any non-governmental organizations (NGOs) working to help beggars?
Yes, several NGOs are working in Uttarakhand to provide shelter, food, healthcare, and rehabilitation programs for beggars. These organizations also focus on skill development, education, and providing opportunities for beggars to lead independent, dignified lives.
What can tourists do to help with begging in Uttarakhand?
Tourists can contribute to the solution by donating to reputable charities and NGOs rather than giving directly to beggars. Supporting long-term initiatives that address the root causes of begging, such as poverty alleviation and education programs, helps create a more sustainable impact.
How can begging be reduced in Uttarakhand?
Reducing begging in Uttarakhand requires addressing underlying socio-economic issues such as poverty, lack of employment, and limited access to education. Creating job opportunities, improving infrastructure, and providing vocational training are essential in helping individuals become self-sufficient and reducing their reliance on begging.
Is begging illegal in Uttarakhand?
Begging is not illegal per se, but the Uttarakhand government has enacted laws to control begging, especially in tourist areas. Local authorities sometimes regulate begging in certain locations to reduce its impact on public spaces and the tourism experience.
How can the public help in addressing begging in Uttarakhand?
Public support through responsible charity and donations to established NGOs is key. Public awareness campaigns can also help educate people on the importance of addressing the root causes of begging and promoting social welfare initiatives to support marginalized communities.
What role does religion play in begging in Uttarakhand?
In Uttarakhand, begging is often seen as part of religious practices, especially in pilgrimage centers. Many beggars, including religious mendicants, view begging as a way to seek divine blessings. This cultural aspect complicates efforts to address begging, as it is deeply rooted in local spiritual beliefs.










